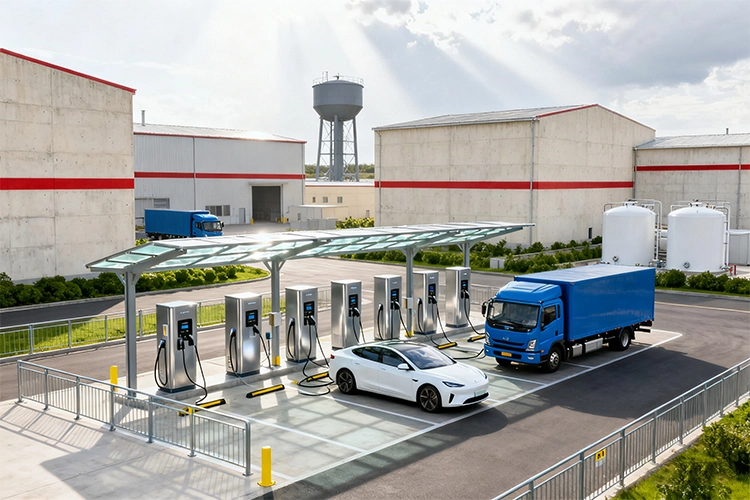
1. Introduction: Why Industrial Parks and Factories Need EV Chargers
The electrification of transportation is no longer limited to urban centers or public highways. As logistics fleets, staff vehicles, and heavy-duty electric trucks continue to grow, industrial parks and large factories are becoming key sites for installing EV chargers.
These areas not only consume massive amounts of energy but also have the space and grid access needed for large-scale charging deployment.
According to Anengjienergy research, more than 38% of new industrial developments worldwide in 2025 will include EV charging infrastructure as part of their sustainability and smart energy plans.
Share of New Industrial Developments Including EV Charging (2025) — Anengjienergy Estimate
Avg installed DC capacity = average aggregate DC power per site for fleet/industrial use.
2. Challenges Industrial Parks and Factories Face When Installing EV Chargers
Installing EV chargers in industrial environments involves a complex mix of technical, financial, and logistical challenges. The most common issues include:
2.1 Power Capacity and Grid Upgrades
Many industrial zones already operate near their maximum grid load.
Installing 200–500 kW DC chargers may require transformer upgrades, new substations, or energy storage integration.
Solutions include photovoltaic + storage + charging systems that offset peak loads.
2.2 Site Planning and Equipment Layout
Heavy machinery areas, logistics docks, and staff parking must be separated from charger zones.
Proper planning avoids downtime and ensures safety compliance (IEC 61851, OCPP 2.0.1, ISO 15118 standards).
2.3 Capital Cost and ROI
The initial investment for installing 10 DC fast chargers (120 kW each) can exceed USD 300,000–400,000, depending on region and power availability.
Without smart load management or energy storage, the ROI period can extend beyond 5 years.
2.4 Maintenance and Operations
Harsh industrial conditions (dust, vibration, humidity) demand IP65-rated, robust charger enclosures.
Remote monitoring and predictive maintenance reduce downtime and improve uptime efficiency.
3. Solutions: How to Overcome These Barriers
3.1 Energy Integration
Utilizar PV + Storage + Charging reduces electricity bills by up to 35% and smooths load curves.
Anengjienergy provides modular systems combining:
Solar generation (50 kW–2 MW)
Battery storage (250 kWh–2 MWh)
Fast chargers (60 kW–720 kW)
3.2 Smart Charging Management
Through OCPP 2.0.1 platforms, operators can:
Balance loads across multiple chargers
Enable scheduled charging for fleet vehicles
Integrate billing, remote diagnostics, and usage analytics
3.3 Flexible Business Models
Factories and industrial parks can choose from:
Self-invested operation (own and profit from the charging service)
Joint venture with energy partners
Leasing models where Anengjienergy supplies, maintains, and shares profits
4. Global Industry Cases
4.1 Europe
Germany: BMW’s Leipzig plant installed 450 kW DC chargers for logistics trucks, achieving a 20% reduction in diesel fleet operations.
Poland: Katowice Industrial Zone added 120 EV chargers to support 25,000 employees and delivery fleets.
ROI: average 4.2 years with government incentives.
4.2 Russia
Tatarstan Industrial Park deployed 40 EV chargers (60–180 kW) for electric forklifts and staff vehicles.
Local grid upgrade cost covered by regional sustainability fund.
4.3 Central Asia (Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan)
Kazakhstan: Almaty Industrial Park installed 20 fast chargers (120 kW each), integrated with solar microgrid.
Uzbequistão: State incentives allow factories to offset 30% of installation cost.
Trend: Government and private partnerships accelerating cross-border logistics electrification.
4.4 Southeast Asia
Thailand: Industrial estates in Chonburi using PV + battery + EV chargers, reducing peak tariffs by 28%.
Vietnam: Major manufacturing zones near Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh are adopting 180 kW chargers for staff and fleet.
Indonesia: Batang Industrial Park offers charging as part of “green industrial” certification.
4.5 East Asia
China leads globally with over 2 million commercial chargers, with many installed directly in factory complexes.
Japan & Korea: Focused on ultra-fast chargers and V2G integration for industrial fleets.
5. 📊 Global Development Trends of Industrial EV Charging (Data for Elementor Charts)
Global Industrial EV Charger Installations (2020–2025)
Industrial EV Charging Market Share by Region (2025)
Industrial EV Charging Business Models (2025 projection)
| Model | Global Share (%) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Invested Operation | 42% | Factories install and operate their own charging infrastructure |
| Shared Investment (JV) | 35% | Collaboration with charging or energy providers |
| Leasing Model | 18% | Equipment supplied and maintained by third-party provider |
| Others (PPP, etc.) | 5% | Public-private partnership or special regional programs |
Profitability Projection by Region (ROI in Years)
| Region | Average ROI (Years) | Incentive Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | 4.2 | Strong | High subsidies and tax benefits |
| Asia-Pacific | 4.5 | Moderate | Large-scale industrial deployment |
| Southeast Asia | 3.8 | High | Lower labor and construction costs |
| Russia & Central Asia | 5.1 | Moderate | Energy tariffs favorable but grid cost high |
6. Profit Models: How Industrial Parks and Factories Earn from EV Chargers
Factories and industrial parks can create multiple revenue streams:
| Model | Description | Typical Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Pay-per-use | Charge per kWh or session for staff and visitors | 20–30% |
| Fleet Charging Services | Provide fast charging for logistics partners | 25–35% |
| Energy Storage Optimization | Sell stored energy during peak hours | 10–20% |
| Advertising / Digital Services | In-app or charger display ads | 5–10% |
| Government Carbon Credit Trading | Participate in green certificate programs | Up to 15% extra revenue |
7. Why Choose Anengjienergy
Anengjienergy specializes in large-scale EV charger installations for industrial environments.
We provide:
DC fast chargers (60 kW–720 kW)
Integrated PV + storage + charging solutions
OCPP 2.0.1 platform support and cloud monitoring
Turnkey EPC and maintenance services
Our engineering teams have delivered projects across Europe, Central Asia, and Southeast Asia, helping industrial clients achieve ROI under 5 years.
8. Future Outlook
By 2030, over 65% of new industrial parks worldwide will include dedicated EV charging infrastructure.
Governments are offering incentives for green industrial certification, and companies adopting Anengjienergy’s scalable solutions can lead in sustainability, profitability, and energy independence.