Introduction
As the global electric vehicle (EV) market continues to expand rapidly, electrification has become a mainstream trend across the transportation industry. By 2025, the global EV fleet has exceeded 42 million vehicles, while annual EV sales in the United States reached 1.43 million units, accounting for 12.7% of total new vehicle sales.
However, public charging infrastructure has fallen far behind this growth. Across the U.S., there are only about 126,000 Level 2 AC charging stations and just over 30,000 Level 3 DC fast charging stations, resulting in a vehicle-to-charger ratio as high as 17:1. This structural imbalance not only creates real challenges for EV drivers—such as difficulty finding chargers and long wait times—but also opens up an unprecedented window of opportunity for EV charging businesses.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of commercial AC and DC EV charging stations, covering cost structures, charger selection logic, policy incentives, and advanced profitability models.
Types of Commercial EV Charging Stations and Application Scenarios
Before deciding which type of charging station to install, businesses must select the most suitable solution based on their operational needs. EV charging is generally divided into three levels, each with different costs, charging speeds, and use cases.
Level 1 Charging Stations: Primarily for Residential Use
Level 1 charging stations are the lowest-cost and simplest option available. Due to their slow charging speed, they are widely used in residential settings. Installation requirements are minimal, as these chargers typically plug directly into a standard wall outlet.
Charging a vehicle to full capacity using a Level 1 charger usually takes around 10 hours, making overnight charging the most practical scenario. With a low power output of 1.3–2.4 kW, Level 1 charging stations are not suitable for commercial use.
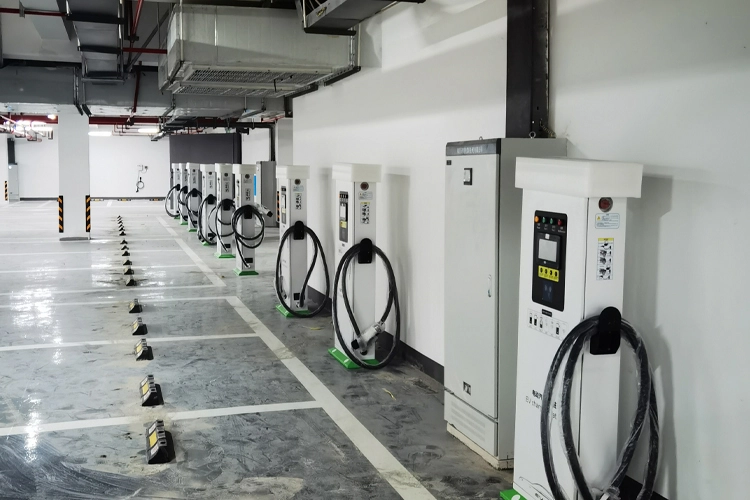
Level 2 Commercial EV Charging Stations for Businesses
Level 2 charging stations represent a mid-range EV charging solution and are the preferred option for small and medium-sized businesses. These chargers require a dedicated 240V AC circuit and must be installed by a licensed electrician.
Level 2 commercial EV chargers can provide 20–40 miles of driving range per hour, allowing a full vehicle charge within 4 to 10 hours. They are well suited for workplaces, multi-family residential properties, retail locations, commuter fleets, and fleets that do not require fast vehicle turnover.
On average, the commercial EV charging station cost for Level 2 installations ranges from $3,500 to $15,000 per charging port.
Level 3 Charging Stations: DC Fast Charging Equipment
Level 3 charging stations, also known as Cargadores rápidos de CC, involve a higher level of investment due to their fast and ultra-fast charging capabilities. DC fast charging stations are widely used in public EV charging environments.
Standard fast chargers can deliver a full charge in approximately 45 minutes, while ultra-fast models can reduce charging time to as little as 15 minutes. Tesla Superchargers are a well-known example of DC ultra-fast charging technology.
Installation is more complex and requires a dedicated high-voltage circuit of up to 900V, as well as combined charging system (CCS) connectors. Installation must be carried out by certified electricians. The average installation cost for DC fast charging stations ranges from $18,000 to over $350,000 per port, making them suitable for travel centers, high-traffic public areas, and fleets that require rapid turnaround.
Charging Station Type Comparison
Level 2 Commercial EV Chargers
Total cost per port: $3,500–$15,000
Power output: 3.3 kW–19.2 kW
Suitable for workplaces, multi-family residences, retail locations, commuter fleets, and fleets without fast turnover needs
DC Fast Charging Stations
- Total cost per port: $18,000–$350,000+
- Power output: 50 kW–500 kW
- Suitable for travel hubs, high-traffic public locations, and fleets requiring fast turnaround
Cost Analysis of Commercial EV Charging Stations
The cost of charging equipment increases with each charging level. Initial installation costs include both equipment procurement and construction expenses. Cost ranges vary depending on installation type, from freestanding chargers to wall-mounted solutions.
Hardware and Technology Costs
Level 1 charging equipment is the most basic option and requires only a standard 120V outlet. However, it delivers only 2–5 miles of range per hour, and a full charge can take 40–50 hours, making it unsuitable for commercial applications.
Level 2 commercial EV chargers require a dedicated 240V AC circuit and professional installation by licensed electricians. These chargers deliver 20–40 miles of range per hour and can fully charge a vehicle within 4–10 hours. The average installed cost remains $3,500–$15,000 per port.
DC fast charging equipment is the most complex and expensive type of charging infrastructure. Installation requires high energy capacity and specialized technical expertise, typically performed by electricians certified for Level 3 installations. DC fast chargers provide the fastest charging speeds, adding 50–250 miles of range per hour and completing a charge in 30 minutes to 1 hour. The average installation cost ranges from $18,000 to over $350,000 per port.
Electrical Upgrades and Site Preparation
Most commercial properties require electrical upgrades to support EV charging, including panel upgrades, additional circuits, or transformer replacements to accommodate increased load demand. A site assessment is necessary to determine specific upgrade requirements.
Site preparation costs may include excavation, conduit installation, and concrete work. Expenses vary based on local labor rates and regulatory requirements. Additional costs may include taxes, permits, inspections, and site restoration or landscaping.
Maintenance and Operating Costs of Commercial EV Charging Stations
After installation, businesses must account for ongoing maintenance and operating expenses. Average annual maintenance costs are approximately $400 per charger, depending on the equipment supplier.
Charging station energy management software subscriptions typically cost around $28 per month. Soft costs include signage, wheel stops, parking blocks, and visible markings such as painted parking lines. Chargers installed in high-traffic public locations may also require extended warranty coverage.
A comprehensive maintenance plan should include regular inspections and cleaning, scheduled software updates, safety testing of key electrical components in accordance with IEC 61851, UL 2202, and IEC 60364-7-722, compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC), inspection of low-voltage cables and connection points, seasonal servicing, and cooling system inspections.
Policy Incentives and Financing Options
The federal government has introduced multiple tax incentives and grant programs to accelerate the deployment of EV charging infrastructure. Under the U.S. Department of Transportation’s NEVI Formula Program, qualifying projects may receive funding covering up to 80% of installation costs.
Commercial EV charging stations are also eligible for a 30% Investment Tax Credit (ITC). State and local governments provide additional incentives. For example, Texas offers multiple rebate programs specifically for EV charger installations.
Businesses may also finance charging station installations through private loans, allowing owners to obtain full equipment ownership with manageable monthly payments. After applying government incentives, private loans can cover the remaining upfront installation costs. Leasing options are another cost-effective approach, requiring lower initial payments and fixed monthly fees.
Revenue Models and ROI of Commercial EV Charging Stations
Businesses can create new revenue streams through commercial EV charging stations. Paid charging services help offset installation costs while generating ongoing income. Operators may choose fixed pricing or usage-based billing models depending on their business strategy and customer needs.
In addition to direct revenue, EV charging stations attract environmentally conscious customers. Millennials and Generation Z, in particular, place a strong emphasis on sustainability and are often willing to pay a premium to support businesses aligned with clean energy values.
The return on investment (ROI) for EV charging equipment can be calculated using the following formula:
ROI = (Total Revenue − Total Cost) / Total Cost × 100
Total revenue includes charging fees and advertising income. Total costs include equipment, installation, maintenance, and other operating expenses. ROI analysis helps determine whether EV charging businesses are a suitable investment.
Smart Charging Systems for Commercial EV Charging Stations
Smart charging technology can significantly increase the value of high-traffic commercial charging sites. For example, chargers can be configured to operate during periods with the lowest electricity rates, optimizing charging schedules to reduce energy costs.
If charging can be completed within a customer’s specified time window, businesses can minimize electricity expenses while improving profit margins. Smart chargers can also notify users when vehicles approach full charge or when a charging session is complete, reducing idle time.
Depending on the pricing model, operators may apply idle fees or per-minute charges to vehicles that remain connected after charging is complete, encouraging efficient charger usage.
For businesses focused on maximizing profitability, integrating solar panels or battery energy storage systems can further offset long-term costs and improve overall project returns. In regions with abundant sunlight, excess electricity can be sold back to the grid through net metering programs, creating additional revenue.
Additional Site Selection Criteria
Beyond capacity considerations, charging stations must meet both operational and customer needs. Key factors include charging time patterns, average daily usage, site size and foot traffic, and typical parking duration.
For shopping centers and supermarkets, installing fast charging stations can increase customer dwell time and in-store spending. For office buildings and hotels, Level 2 charging stations offering longer, stable charging sessions may be more appropriate.
Conclusion: Moving Toward a Sustainable Future
In 2025, commercial AC and DC EV charging stations have evolved far beyond basic infrastructure. They now function as integrated platforms connecting customers, data, energy, and consumption.
While upfront investment can be substantial, policy incentives, technological maturity, and strong market demand make it possible for a well-planned charging project to reach breakeven within three to five years and generate long-term value over the next decade.
For forward-looking businesses, the question is no longer whether to invest, but how to build charging infrastructure that is smarter, more profitable, and more sustainable. The future has already arrived—it now belongs to those willing to act first.